This year, the second newborn has died from enterovirus "Echovirus 11." Doctors are concerned it may trigger a pandemic.
- byVic
讀後心得
The Centers for Disease Control announced today (25th) that this is the second case this year of a newborn dying from severe complications due to enterovirus infection. In the past three months, the enterovirus outbreak has resulted in two deaths and one severe case, all involving infants infected with "Enterovirus 11." Doctors remind us that since the end of last year, the number of enterovirus infections in the country has increased, which could lead to a pandemic. Experts from National Taiwan University Hospital pointed out that although we have not yet reached an epidemic alert level, newborns face a higher risk of Enterovirus infection, which could lead to severe consequences. They call on parents to be more vigilant, especially for infants under three months old. Meanwhile, the CDC recommends that pregnant women and caregivers of newborns should strengthen hygiene habits to reduce the risk of infection.
The Centers for Disease Control announced today (25th) the second case this year of a newborn death due to severe complications from enterovirus infection; the baby was declared dead just one week after the onset of the illness. Within three months, the enterovirus outbreak has resulted in a total of 2 deaths and 1 case of severe illness, all related to "Echovirus 11." Doctors remind that since the end of last year, the proportion of echovirus infections in the country has been gradually increasing, with cases of severe illness and death continuously occurring, necessitating heightened vigilance to prevent the spread of the outbreak.
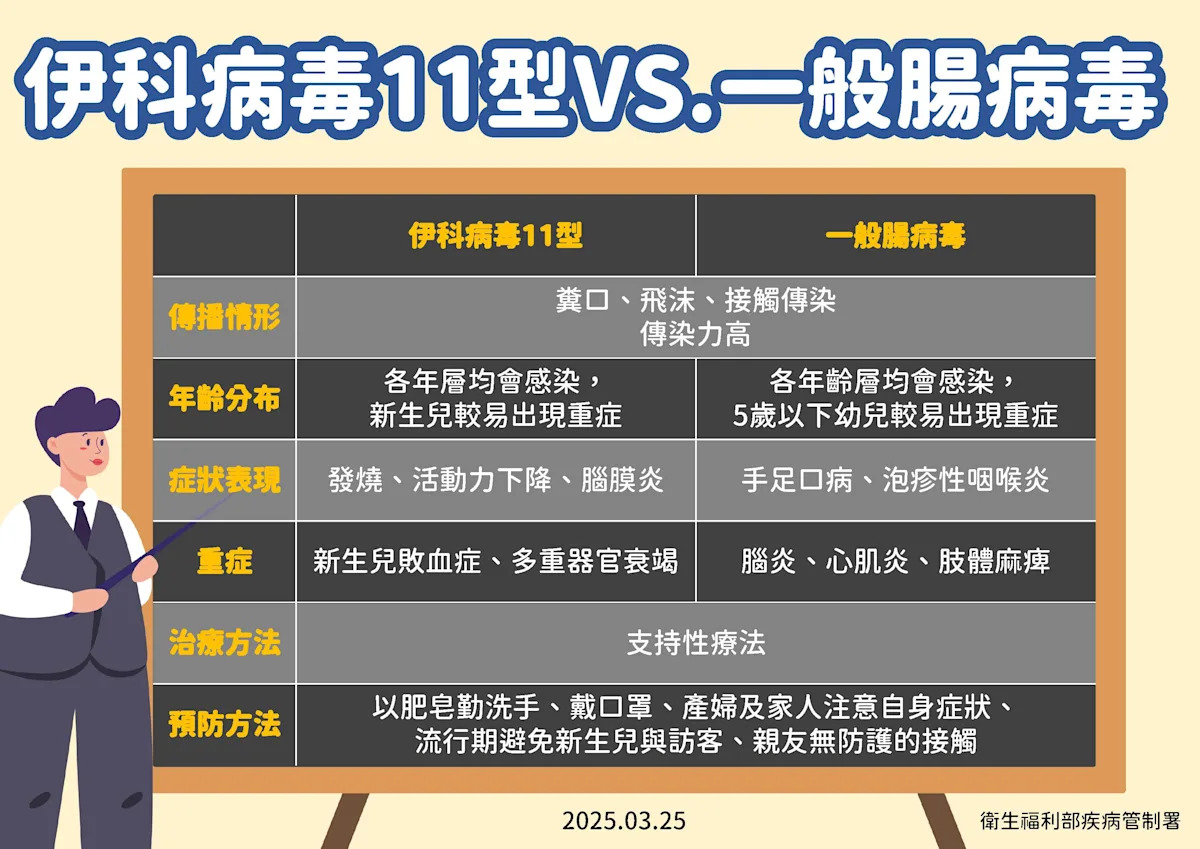
According to the observations of a pediatric infectious disease physician at National Taiwan University Hospital, past enterovirus outbreaks typically start in April and peak in June. Although the current situation has not reached an epidemic alert level, the number of echovirus infection cases has been gradually increasing since the end of last year, with 3 cases of severe illness reported this year, all of which are infections of Echovirus 11, differing from the more common Enterovirus 71 or D68 seen in previous outbreaks.
Physicians note that the transmission route of echovirus is similar to that of other enteroviruses, mainly spreading through respiratory secretions or feces of infected patients. For older children and adults, the symptoms of infection are typically mild, potentially manifesting as a mild fever or discomfort. However, for newborns up to 2 to 3 months of age, infection with echovirus can lead to serious consequences; if not detected and treated promptly, it may cause hepatitis, encephalitis, myocarditis, and could progress to coma, sepsis, and multiple organ failure, posing a risk of death.

According to data from the CDC, since 2012, 60% of severe echovirus cases have occurred in newborns under one month old. The last significant outbreak of echovirus in the country occurred in 2018. Doctors point out that if the virus remains endemic in Taiwan for an extended period, antibody levels will gradually decrease. A study conducted by National Taiwan University Hospital in 2021 found that the antibody rate in women of childbearing age against echovirus is relatively low, raising concerns about a potential outbreak this year, thus urging parents to be especially cautious with infants under three months old.
The deputy director of the CDC stated that the number of enterovirus consultations in the country is slightly lower than the same period last year and has yet to reach the epidemic alert level, but ongoing monitoring of the outbreak's development is necessary. The CDC calls on pregnant women, newborns, and their caregivers to particularly avoid contact with infected patients and to maintain good hygiene practices. Especially during pregnancy and around childbirth, pregnant women should enhance hand and respiratory hygiene and seek medical assistance promptly when experiencing fever or respiratory infection symptoms. Additionally, adults and children should wash hands regularly and avoid contact with newborns to reduce transmission risks.

Institutions such as hospital nurseries, daycare centers, and postpartum care homes should implement visitor management and infection control measures. If a cluster infection of enterovirus is identified, timely reporting and appropriate preventive measures should be taken.