Knee swelling and pain alert! It could be an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament. Doctors recommend this treatment to prevent joint degeneration.
- byVic
讀後心得
Mr. Li, 64 years old, sought medical attention due to knee instability and pain. An examination revealed 50cc of joint effusion and a mild tear of the anterior cruciate ligament. The doctor indicated that ligament injuries are a common knee joint problem, and if long-term instability occurs, it can accelerate degeneration. Common treatments include anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy; if ineffective after two weeks, regenerative therapies such as high-concentration glucose solution and PRP treatment may be considered. The doctor reminded that if knee pain persists for more than two weeks, one should seek medical attention promptly to avoid worsening the condition.
Mr. Li, 64 years old, has been feeling instability in his left knee, sometimes accompanied by pain. Recently, he went to the hospital's rehabilitation department for a check-up due to a recurrence of swelling and pain in the knee. An ultrasound examination showed severe fluid accumulation in the knee, and the doctor used a needle to extract 50cc of joint fluid. Subsequent X-ray and MRI examinations revealed that he had mild degeneration of the knee and partial tears in the anterior cruciate ligament. Additionally, the meniscus and collateral ligaments were also injured.
The rehabilitation physician pointed out that tears or ruptures of the cruciate ligaments are common knee injuries. According to foreign studies, approximately 200,000 people each year require surgery due to anterior cruciate ligament ruptures. If the cruciate ligament is damaged, the muscles in the leg must bear the responsibility of stabilizing the knee, leading to knee pain. Long-term instability in the knee can accelerate joint wear and tear. When it becomes severe enough to cause fluid accumulation, symptoms typically include limited knee movement, difficulty in mobility, and knee swelling, with acute phases possibly accompanied by redness and pain.
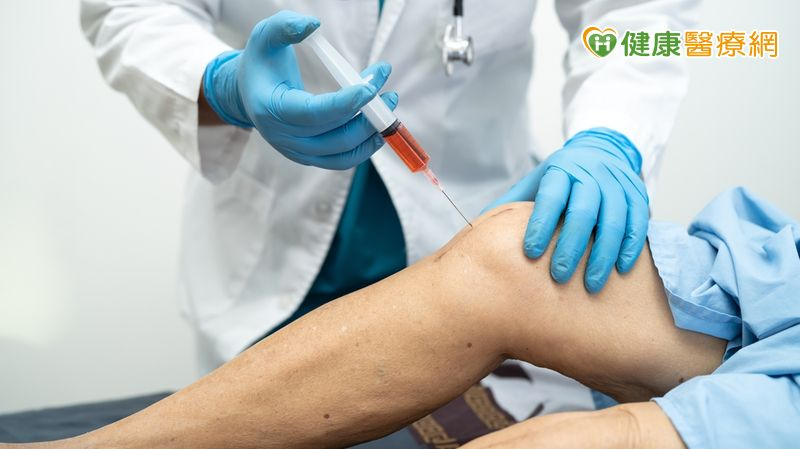
If treatment for more than two weeks is ineffective, prolotherapy may be considered. When the knee is examined due to swelling and pain, ultrasound, X-ray, and MRI examinations are usually conducted. Nowadays, if soft tissue is damaged, prolotherapy is commonly chosen. The doctor explained that traditional treatment mainly relies on anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving medications along with physical therapy to alleviate pain, supplemented by exercise training to strengthen the quadriceps and hamstring muscles to stabilize the knee. For more serious tears, if there is no improvement after more than two weeks of treatment, the use of prolotherapy, such as high-concentration glucose solution and PRP, may be considered.
PRP therapy involves separating platelets from about 10cc of the patient's own blood and injecting them into the injured area. These platelets contain growth factors that promote cellular proliferation and repair, thus being widely applied in the treatment of various joints and ligaments. Since it uses autologous blood, PRP is considered a relatively safe treatment option. However, it is not advisable for patients with chronic diseases, immune disorders, or those taking antiplatelet medications. Generally, injections are required every 2 to 6 weeks, with 3 to 4 treatments needed, depending on the condition. Additionally, there may be soreness and swelling after the injection, necessitating continuous rehabilitation and follow-up visits, along with maintaining good nutrition and adequate sleep to enhance effectiveness.
The doctor reminds that the human body possesses compensatory mechanisms; even if walking is temporarily impossible after an injury, there is often a certain degree of recovery ability, which can lead to the injury being overlooked. If knee pain persists for more than two weeks without improvement, a medical examination should be sought as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening.